Maslow Free Study Guide for UNISA
Abraham Maslow’s difficult childhood
“Maslow was the eldest of seven children born to his parents but he had a rather lonely and unhappy childhood.…
Continue Reading for more human drama and insight…
Maslow, behaviorism and animal cruelty?
While he was a student, Abraham Maslow belonged to the behaviorist school of thought. He continued to work and study under Harry Harlow up to PHD level. Harlow is famous for his experiments on baby monkeys that had been removed from their mothers.
He himself researched the sexual and dominance characteristics of baboons, from a behaviorist perspective.
But when Maslow’s first child was born, he moved away from behaviorism decisively and permanently.
And forged his way as one of the pioneer humanists of his time -diametrically in opposition to the mood, premises, goals and worldview of radical behaviorism.
Guess first: Unisa questions:
QUESTION 11
Which one of the following statements correctly reflects Maslow’s view?
(1) Self-actualisers function relatively independently of their physical and social environment
(2) Self-actualisers are achievers who will use any means to reach the high goals they have set themselves.
(3) Self-actualisers are sociable people who like to have constant contact with other people.
(4) Self-actualisers tend to be autocratic since they are functioning on a higher level than most people.
[democracy id=”1″]
Answer
QUESTION 12
According to Maslow, the person who functions optimally
(a) can meet his or her deficiency needs regularly.
(b) has accepted the responsibility of self actualisation.
(c) is functioning at the level of self-actualisation.
The correct answer is:
(1) (a)
(2) (b)
(3) (a) and (c)
(4) (a), (b) and (c)
[democracy id=”1″]
Answer
QUESTION 13
According to Maslow, self-actualisation is not always attained because
(a) most people evade responsibilities and shy away from the challenge to realise their talents and work towards self-actualisation.
(b) the social environment can place obstructions in the way of a person’s growth towards self-actualisation.
(c) it is a developmental achievement which only exceptional people attain. The ordinary person does not feel the need to function on the higher levels of self- actualisation.
(d) most people have poor self-knowledge and do not know what they are capable of and consequently fail to realise their potential.
The correct answer is:
1) (a) & (b)
2) (b), (c) & (d)
3) (a), (b) & (d)
4) (a) & (c)
[democracy id=”1″]
Answer
Question 14
Maslow believes that meta-needs
(1) are not linked to self-actualisation
(2) must be fulfilled to ensure maximal growth
(3) if unfulfilled, will not lead to pathological conditions
(4) unlike basic needs, are not innate
[democracy id=”1″]
Answer
QUESTION 15
Which one of the following statements relating to Maslow’s conceptualisation of self- actualisation, is INCORRECT?
(1) The fulfilment of basic needs will lead to the next step, namely, the achievement of self-actualisation.
(2) Self-actualisation is a growth need which leads to fully-functioning, goal oriented being.
(3) Even though self-actualisation has been achieved, a severe set-back in life may cause regression to a lower level of need.
(4) A person may have fulfilled every deficiency need yet feel restless and unhappy.
[democracy id=”1″]
Self-actualisers
- We should study people who have reached their highest potential, understand how they did this, and learn from them.
- Maslow called these people self-actualisers.
- People are essentially naturally good unless stressed, in pain or in a society that does not enable goodness.
- Each of us is responsible for our success.
- We all have a natural yearning to be the best we can.
- Striving to gratify our needs drives growth.
- Understand people holistically as whole beings, not as fragments of biology, drives and impulses.

| School of psychology: | Psychoanalytical | Radical Behaviorist | Humanist |
| Who and What to study? | Psychopathology holds up a mirror to humanity which gives us understanding of our unconscious drives and the structure of the human psyche. | – Studying caged animals – Presenting stimuli. -Record and quantify fixed, reproducible responses. | Study healthy people (optimally functioning self-actualisers) to learn the real potential of humanity. |
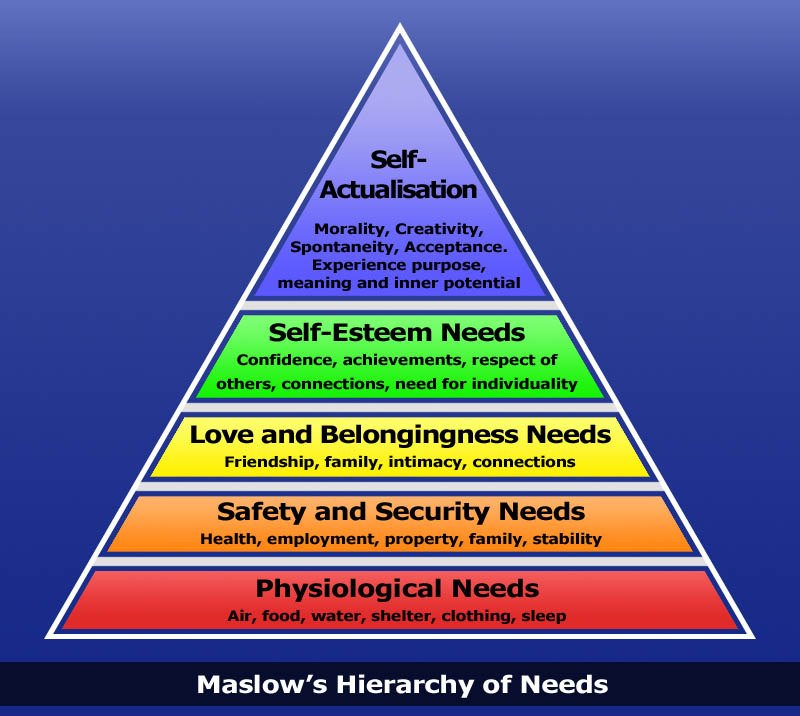
In general, you need to fulfill each lower need on the pyramid before you can fulfill the next – but of course not always. Mandela accepted years in prison to retain his integrity.
Two types of motives:
- deficiency: First 4 levels are motivated by deficiency. Once your need for 1 to 4 are fulfilled, motivation falls away.
- physiological well-being,
- safety,
- love and affiliation
- self-esteem
- Growth motives: level 5
- 5. self-actualization
1. Physiological needs
These are needs focused on survival and bodily integrity. Sexual needs fall into this category, but sexual behavior is motivated by needs higher up on the pyramid.
2. Safety needs
This is not only physical safety, but also stability, structure, predictability and social order.
3. Need for love & belonging
Need to belong, give and receive love, be part of a group, and connect with others.
4. Need for self-esteem
The esteem of oneself – feeling like you can do things, succeed, be strong and independent.
The esteem of others – social standing, importance, being appreciated and respected.
5. The need for self-actualisation
There are 17 growth motivations – also called meta-needs, or B-values.
- Truth
- Justice
- Meaningfulness
- beauty
- order
- simplicity
- perfection
- wholeness
- completion
- totality
- uniqueness
- Aliveness
- goodness
- autonomy
- humour
- effortlessness
- knowledge and understanding

Self-actualization is the process of becoming all you can be – making full use of your talents and potential.
Development of personality
As babies develop, they develop according to the hierarchy of needs. But people need more than their basic needs met. They need to fulfill their meta-needs too.

People can regress to lower levels on the hierarchy if their needs are not met.
And this is not a rigid prescriptive structure of understanding – there are always exceptions etc – the point is that people and children should have their needs met.
Why do people fail to self-actualize?

- Lack of self knowledge and insight – depending on external values and instructions on who and how to be.

3. The Jonah complex: Running away from your talents and thus also from your responsibilities
Optimal Development
Self actualized person gets all needs met and has many of these 15 characteristics:
- realistic observer, and can tolerate not knowing/uncertainty
- accepting self, others & human nature
- spontaneous and authentic
- involved in a task or calling
- able to enjoy isolation and disengage from people
- independent of environment & society
- appreciate the basic beauty of life every day
- peak experiences
- concern for humanity
- small circle of intimates (interpersonal relationships)
- democratic and egalitarian
- moral discrimination
- kind and philosophical sense of humour
- playful creativity
- resist convention when necessary
Maslow on psychopathology
He thought about how people limit themselves.
People become pathological because of unmet needs.
Or because of overgratification of needs and lack of boundaries.
(And this is also true of the higher meta-needs)

Maslow’s Theory Applied
The emphasis on people’s needs has been widely applied in the workplace, education and psychotherapy.
In education, students should be encouraged to reach their potential.
The therapist :
- is a facilitator of growth
- a guide towards insight. (Insight therapy)
- and helps the client get his or her needs met (need therapy)
- Religion: As an intense personal experience Religion is part of self-actualisation. (Good) As a social convention, it is a defense and a limitation on authenticity.(Bad)
- Research:
- Maslow could see the value of quantitative hard research, like behaviorism.
- But from his view, experiential, holistic research that enables an insight into the subjective world of the people being evaluated would be most useful.
- He came up with questionnaires to evaluate a person’s degree of self-actualisation
- And for needs assessments
- Aggression: People do have a destructive and dark side. Sometimes aggression may be caused by unmet needs. We are responsible for our choices and actions.
Short test to measure self-actualization
The original 1965 Personal Orientation Inventory test is 150 questions, and you can’t access it for free. Here is a very quick free short test:




