Substance-use Disorder
Cognitive, behavioral and physiological symptoms due to continued substance use, even while the substances are causing harm.
- Mild – Two or three symptoms
- Moderate – four or five symptoms
- Severe – six or more symptoms
Substance-induced disorders
Intoxication, withdrawal and substance-induced mental disorders
Substance-Related Disorders
Either substance-induced or substance-use disorders
DSM-5 Criteria for a substance-use disorder
At least 2 of the following over 12 months causing significant impairment/distress:
- Using more or for longer than intended
- Unsuccessful attempts to control substance due to cravings
- Spending a lot of time getting, using or recovering from using
- Craving/strong desires to use
- Dropping out of responsibilities because of substance-use
- social and interpersonal harm
- impaired work, social and leisure activities
- physical endangerment due to substance use
- Continued use even though physical and psychological harm is occurring
- Tolerance causing increased need for the substance
- Withdrawal symptoms when the person tries to stop using, which trigger the person to start using again

What to remember
The essence is :
- impairment & distress,
- compelled by the substance/behavior
- keeps getting worse

Gambling addiction
The gaming industry tries to feed into the gambling industry as gamers will know – for gaming, sex, or eating addictions, you can use the same rules of thumb.
Minimum criteria for a diagnosis
4 of the symptoms for a year.
- Tolerance causing increased need to gamble more money
- Withdrawal symptoms of irritability & restlessness when the person tries to stop gambling
- Gambling more or for longer than intended
- Unsuccessful attempts to control gambling
- Spending a lot of time gambling, thinking about gambling, finding money for gambling etc
- Self-soothes with gambling when upset or distressed
- Can’t stop coming back, tries to win back losses
- Deceives others about the financial losses, extent of behavior etc
- Has lost jobs, relationships etc
- Has to get financial help because of gambling
Severity of gambling addiction
- mild: 4-5 symptoms
- moderate: 6-7
- severe 8-9
Substances that people abuse
Different substances have very different risk profiles and effects. Some people cannot touch any mind-altering substances at all -they are at high risk of developing a substance-dependency.
Some substances are dangerous to anyone who uses them. Heroin, for example, carries the risk of overdose or dependency once it is used past a particular fine line of quantity and number of doses, for any person at all.
Crack (crystalized cocaine) is instantly addictive for some people.
Human societies have been using mind-altering substances, such as alcohol, for thousands of years. Most people come through unscathed, but never all.
- Depressants:
- Alcohol
- opioids – heroin, opium, fentanyl, oxycontin etc
- sedatives, hypnotics, anxiolytics
- Stimulants
- caffeine
- amphetamines – eg tik – crystal meth
- cocaine
- crack (cocaine crystals)
- Hallucinogens
- LCD
- psilocybin
- mescaline
- salvia
- Dissociative anaesthetics
- Phencyclidine (PCP)
- Ketamine, methoxetamine (MXE)
- Dextromethmorphan
- Substances with multiple effects
- nicotine
- cannabis
- inhalants
- Ecstacy (MDMA)
- Gamma hydroxybutyrate (GHB)

Etiology of substance-Use Disorders
The progression from substance-use to addiction is not always typical, but the typical progression goes something like this:
- Initial use: The decision to experiment
2. Increasing use: Using the substance for a purpose – to numb painful emotions, to feel more confident or less anxious, to have fun, etc

3. Heavy Use: The brain chemistry begins to be altered, often causing physiological dependence, cravings, and withdrawal.

4. Drug Lifestyle: Lifestyle changes – life changes to follow the demands of the addiction, and as chronic use of the substance damages the person’s ability to function socially, professionally etc.
The 4 dimensions
Psychological Dimension
Substance use is often self-medication as a coping strategy.
It may be a response to mental illnesses or disorders, and/or to stressors. Or be used as tool to cope with life transitions. Or to regulate behavior – such as social drinking to overcome shyness.
Behavioral undercontrol is a personality characteristic associated with rebelliousness, novelty seeking, risk-taking and impulsivity. People with these traits are more likely to experiment with substances.
We can divide life-stressors that lead to substance use and misuse into:
- General life stress – work, relationships etc
- trauma and catastrophe
- childhood stressors and trauma
- discrimination

Social Dimension
Victimization, stress in childhood, including neglect and abuse are strongly associated with substance-use in adulthood.
Substance abuse often begins in adolescence and early adulthood.
Experimentation is part of the rite of passage for many youngsters of moving away from the family, forming a new identity and becoming part of a social group of peers.
Some families see this behavior as expected and normal, or do not play a disciplinarian role for their youngsters. These patterns of family behavior and norms are associated with a higher likelihood of risky behavior.
- peer pressure, and emulation
- wanting to fit in
- rebelling and challenging authority
- asserting independence
- experiment and question social norms
- escape pressure to conform and achieve
- have fun
- take risks

Sociocultural dimension

The media is also a powerful normative driver of substance use.
Biological Dimension
Substances change brain functioning. Many drugs increase dopamine, which is associated with rewards for behavior and with pleasure.
Tolerance: When the brain is exposed to lots of dopamine for a while, it starts reducing the number of receptors to restore balance. So then the person becomes dependent on the substance to feel normal. When they try to stop they feel dreadful, and go through withdrawal.
Different substances can cause different kinds of brain damage and damage to the body. And the withdrawal symptoms vary for different substances. Alcohol withdrawal can actually be life-threatening.
There does seem to be some genetic proclivity to addiction. And different genetic abilities to metabolize specific substances
Women are more vulnerable to addiction and less able to detoxify from many substances.
Treatment
Substance-use disorder is entirely preventable, in theory anyway, by abstinence.
Recovery from active addiction is another matter entirely.
Narcotics Anonymous and Alcoholics Anonymous are long-standing peer-support organizations that help people recover from addiction.
There are also many drug rehabilitation organizations that help people. However, they are often very expensive.

To get clean, many people have to change their whole lives.
They need to find a sober social support network, end relationships with co-users, heal the emotional traumas and mental disorders that led them into addiction in the first place, and self-regulate intensely to avoid the exhaustion of will-power that leads to relapse.
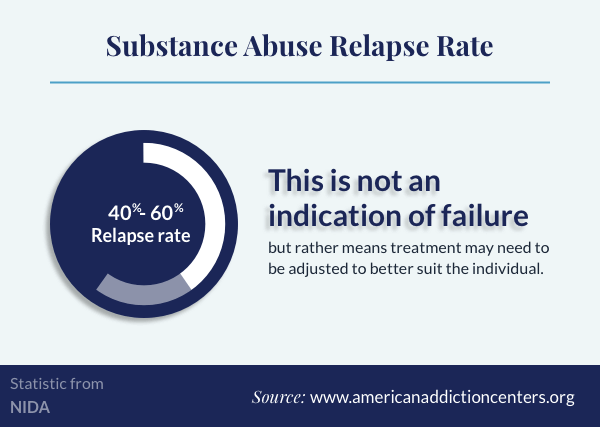
Relapse is frequent, and usually leads back to usage of the substance. It is also very dangerous in the case of opioids, and frequently causes an overdose because the person can no longer tolerate the same dose as before.
Medications can help people through the withdrawal and early stages of abstinence.
Motivational enhancement therapy can help people in the process of making the decision of whether or not they want to get clean. The person needs to work through their ambivalence before starting the process, and this can help with this process, reducing the risk of relapse.

Drugs in South Africa – effects & risks
(Important for exams)
Parts of South African society are being destroyed by drugs, as we all know all too well. I am going to do my best to cut this down to what we may be examined on, not what we would like to understand better.
Heroin:
- Ultimate painkiller, euphoric, then causing rebound depression.
- Addictive after a few weeks of use.
- Margin between feeling good and death by overdosing causing respiratory depression/ failure to keep breathing is very fine.
- sharing needles increases risk of HIV &hepatitis
- liver damage, seizures, coma, death
Marijuana
- relaxing mild hallucinogen
- increased risk of psychotic disorders
- long term damage of learning and memory
- increased risk of heart attack and lung disease, including cancer
- infertility
Cocaine
- Stimulant – creates confidence and euphoria, rebound depression
- addictive
- sexually stimulating
- heart & lung disease
- brain damage
- expensive
Solvents
- glue, benzene, nail polish remover(acetone), spray paint
- street children sniff off a piece of cloth
- dizzy & drowsy
- can’t concentrate, memory impairment, brain damage
- weight loss
- bone marrow damage

Mandrax (buttons)
- Methaqualone
- Central nervous system depressant
- relaxation & euphoria, salivation followed by feeling weak, stomach pains, vomiting
- cheap, but you need more and more
- epilepsy, emotional problems, insomnia, toxic psychosis
Ecstacy – MDMA
- rave drug for all night dancing
- mild euphoria, hallucinations, prosocial feelings, with rebound depression
- rare risk of dehydration/overhydration and death
- long term risks of brain damage, kidney failure, psychosis, convulsions
Tik -methamphetamine
- stimulant giving feelings of confidence, power, sexuality
- memory loss, weight loss, dental and skin problems, stroke
- specifically high co-morbidity with anti-social personality disorder (not in exam)
Nyaope
- South African street drug cocktail: unpredictable mix of heroin, dagga, mandrax, antiretroviral drugs, etc, so highly addictive and cheap
- swallowed, smoked or injected
- Extremely high risk of injury or death
